Patch management tools are used to ensure that an organization’s IT infrastructure and software components are up to date. These tools function by keeping track of middleware and software upgrades. They then notify users when updates are required or carry out updates automatically. These tools are used by businesses to lessen the burden on staff members to update software and guarantee that known vulnerabilities are fixed. A product must meet the following requirements to be Patch Management software category:
- Keep track of updates to hardware, middleware, and software.
- Automatically notify users of new updates or software patches.
- Alert administrators to any endpoints or users that are using outdated software.
1. Spiceworks Network Inventory
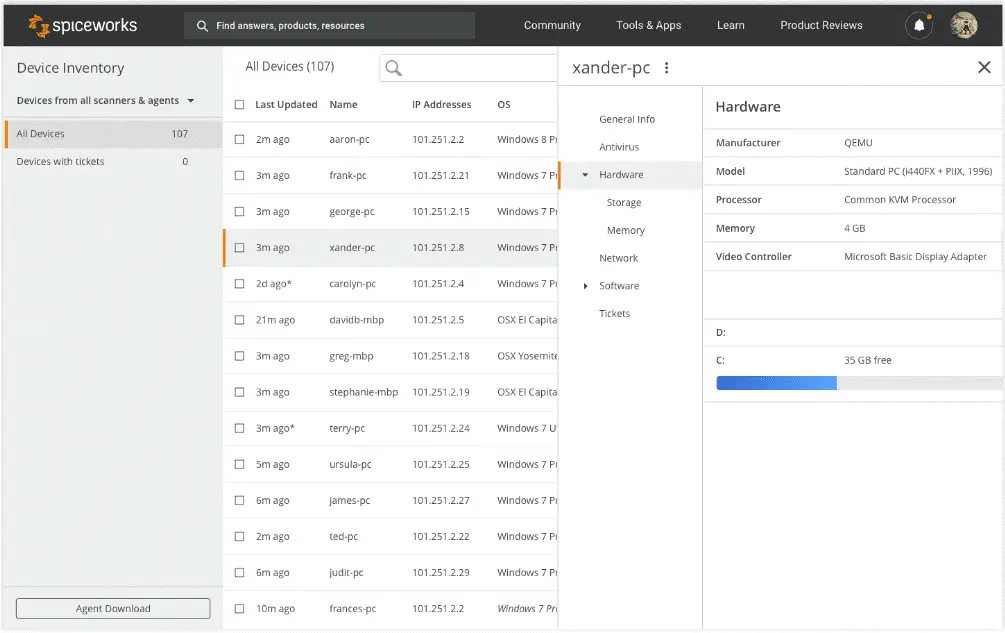
A network discovery program called Spiceworks Network Inventory enables you to search for Windows, macOS, Linux, and Unix devices by IP range. You may make sure you are ready by conducting scans on a sporadic basis or scheduling them for later. Software for Windows and Mac devices can be updated automatically by Spiceworks Network Inventory after you have done scanning the devices. Additionally, you can manually check the OS of devices using the main table view. One of the most lightweight software update checkers for devices is Spiceworks Network Inventory. The fact that it is free is another benefit. The program is accessible to Windows users.
2. ConnectWise Automate
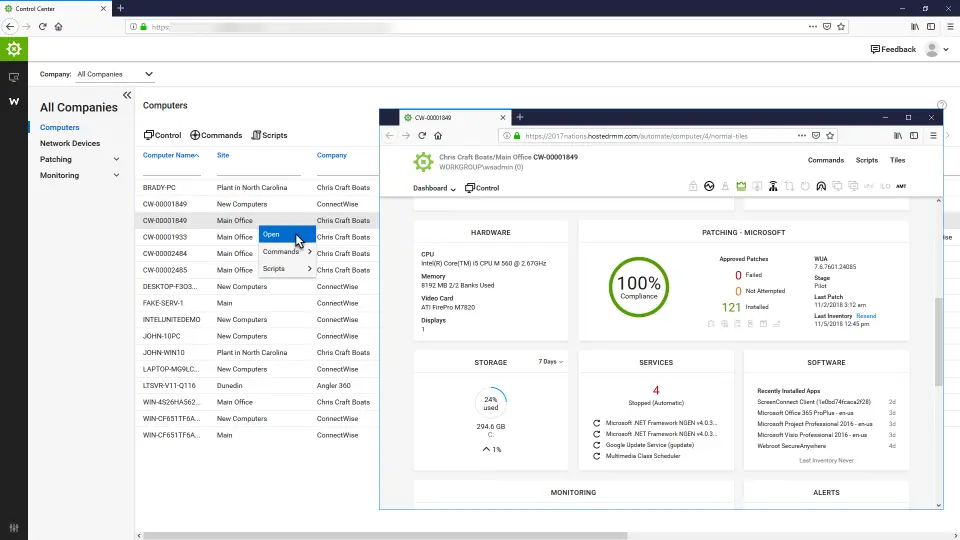
An RMM solution called ConnectWise Automate can update third-party programs automatically. Programs supported by ConnectWise Automate include Adobe Flash, Adobe Reader IX, and DC, Apple iTunes, Google Chrome, Mozilla Thunderbird, Mozilla Firefox, Microsoft Skype for Business, PDF Creator, and VLC Media Player.
3. Atera – FREE TRIAL
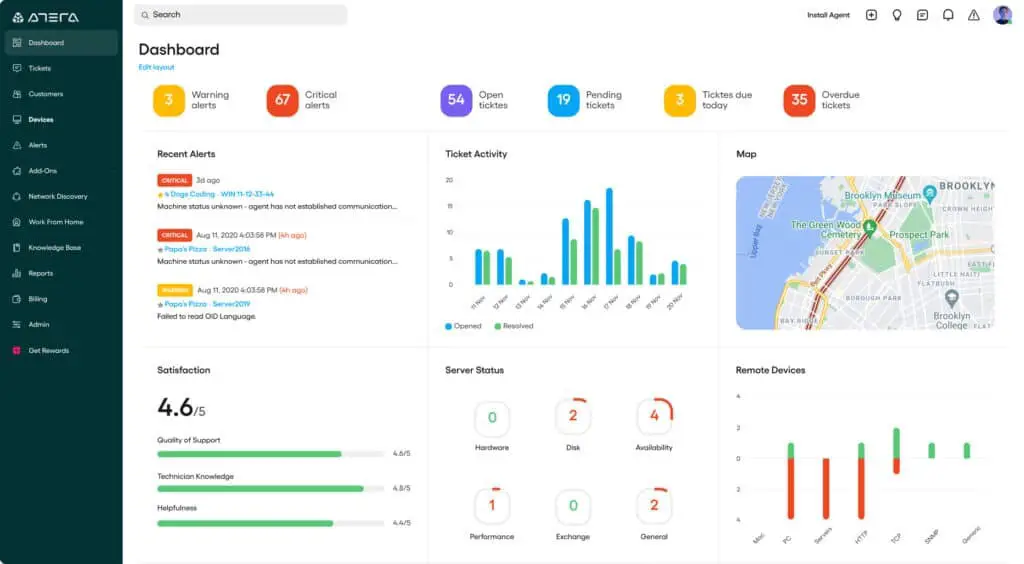
A managed service provider (MSP) firm can be supported by Atera, a complete set of tools. A patch manager is one of the technician tools offered by this cloud-based service. A technician can coordinate patch management for multiple clients on the same console because this system supports multiple tenants. The tool’s automatic processes make finding and installing patches a breeze. The network’s devices are all scanned by the patch management system, which records the versions of each device. This makes it possible for the patch manager to look for fixes to bring those systems up to date.
4. ITarian
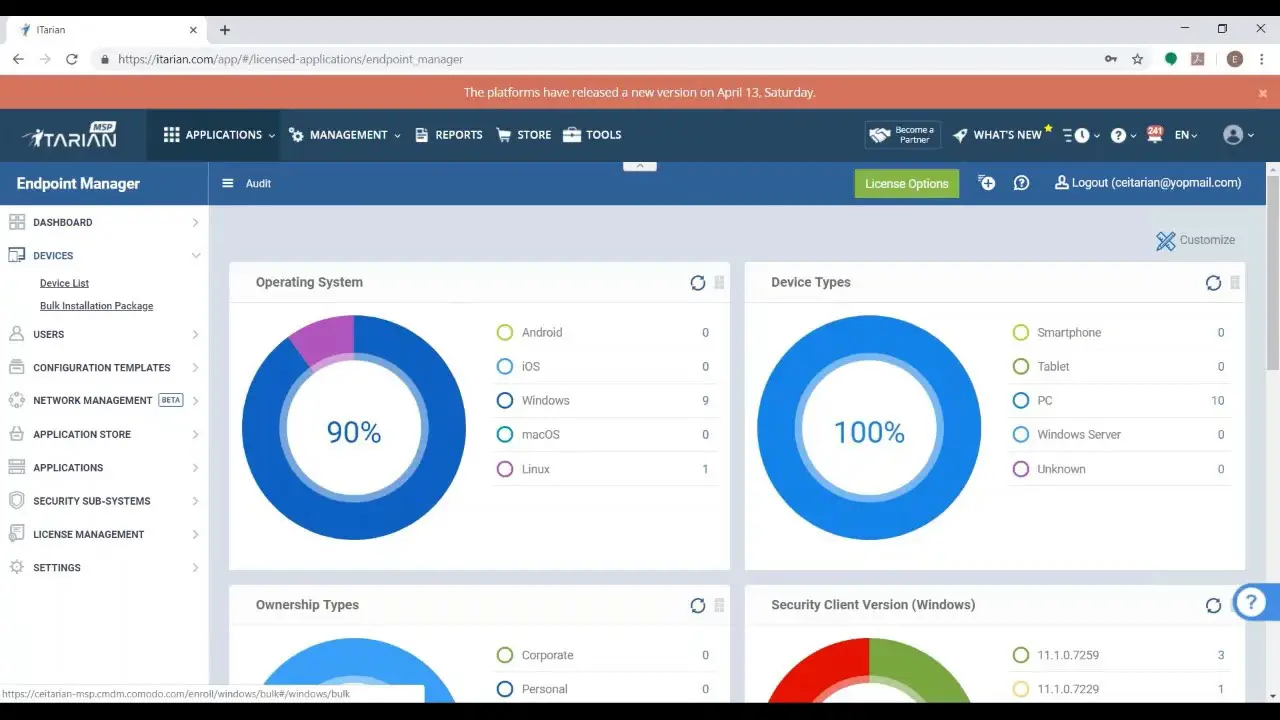
Microsoft Security Bulletin, third-party software, and updates for Microsoft software can all be found using ITarian, a patch management solution for Windows. You were automatically locating connected devices and spotting those in need of patches, ITarian. When you find unpatched gaps, you can take steps to close the vulnerability. You may schedule patches so that they automatically install and run every day. To ensure that your most critical assets are patched first, you can also prioritize updates depending on severity, kind, or vendor.
5. NinjaOne Patch Management
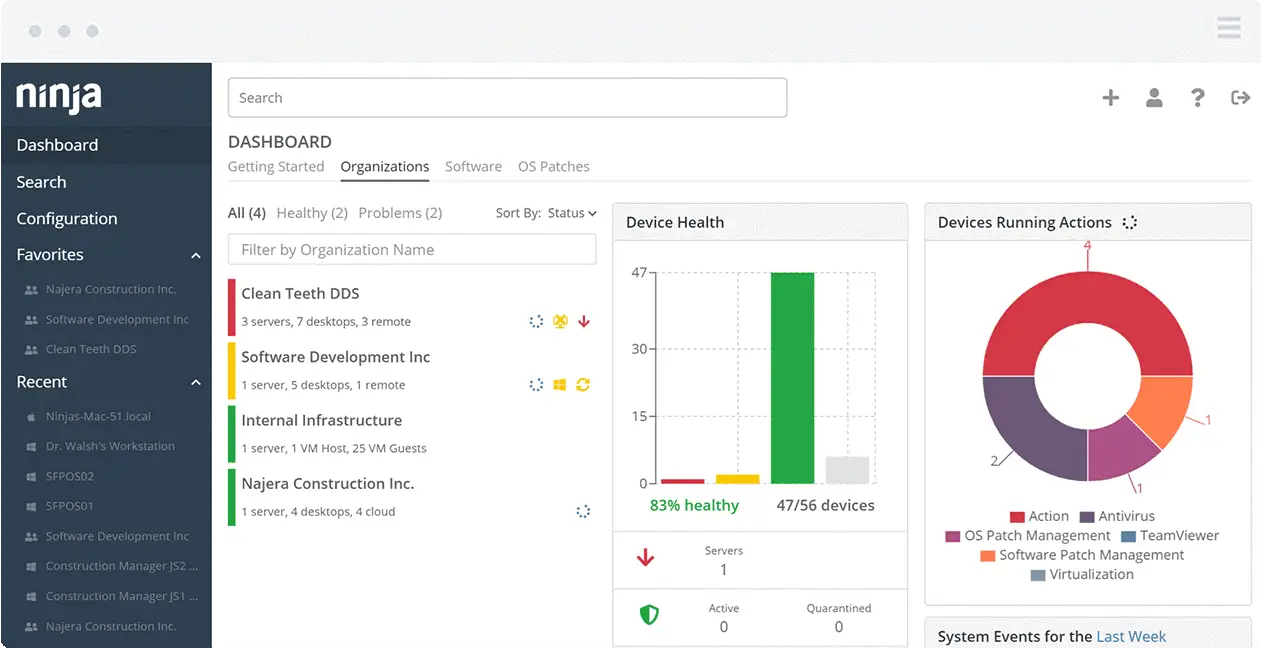
NinjaOne, formerly known as NinjaRMM, is a platform for remote monitoring and management (RMM). It provides all the equipment needed by technicians to support IT services. The managed service providers (MSPs) who work in various distant sites require this set of tools, but IT departments could also use it. A patch manager is part of NinjaOne’s service package.
6. SuperOps RMM Patch Management
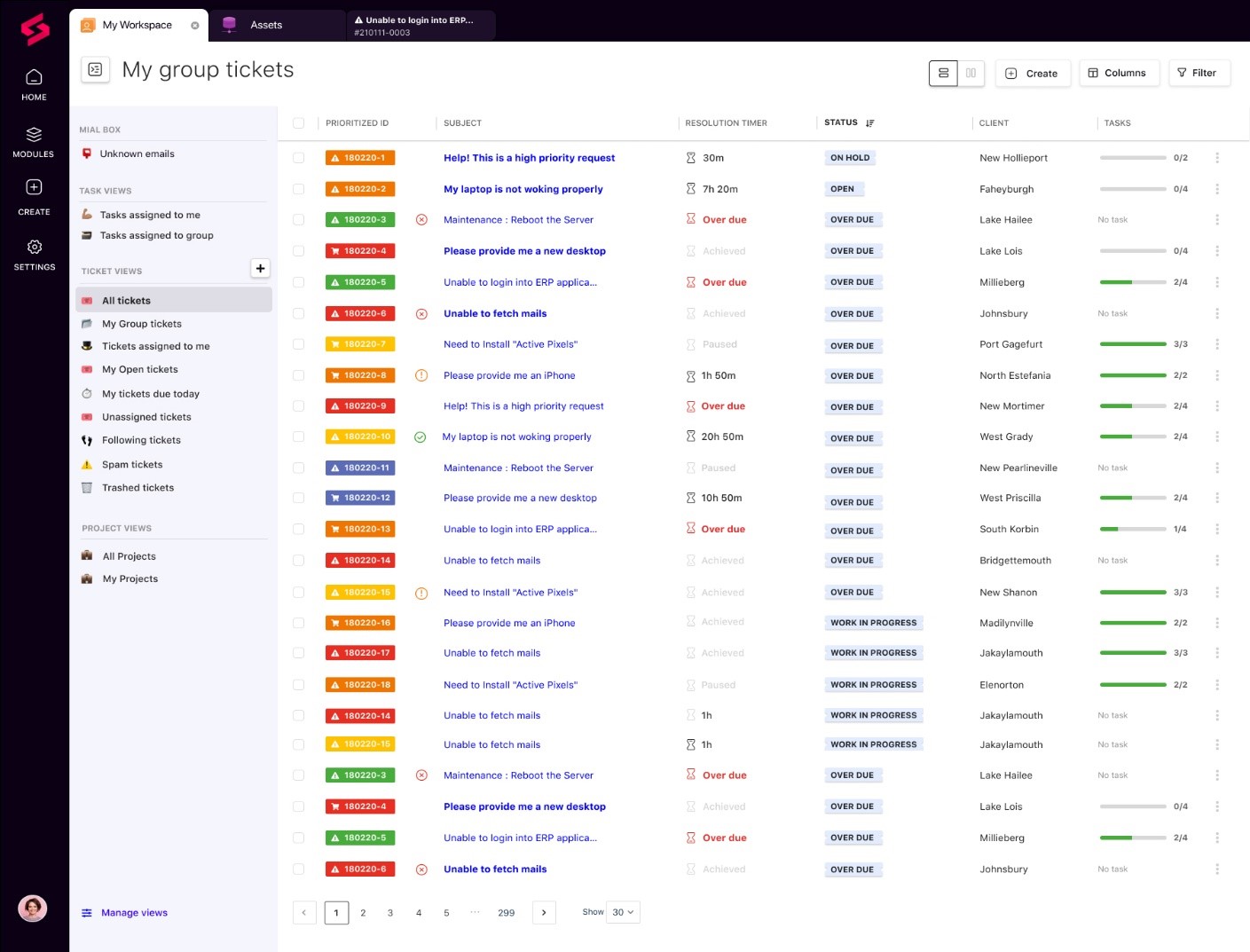
SuperOps RMM’s Patch Management solution is a component of a SaaS platform that also has a PSA system. These two versions combined offer extensive services to MSPs. The SuperOps system can be altered. The platform comes with many automated processes, but thanks to its scripting language, users can modify or even add new automation operations. The Patch Management tool is flexible since it offers options for how the system will function and provides necessary automatic procedures.
7. GFI LanGuard
A patch management program called GFI LanGuard automatically locates devices linked to your network. You can find updates for Windows, macOS, and Linux devices using GFI LanGuard. Devices can receive updates automatically. If a patch interferes with your operations, you can revert to a previous version using the roll-back option.
8. SolarWinds Patch Manager
Patch Manager (PM), an award-winning product from SolarWinds, is feature-rich and simple to use. SolarWinds PM supports a wide range of third-party programs in addition to Microsoft patching, streamlining, and centralizing the entire patch process from download to patch.
9. SecPod SanerNow Patch Management
SecPod SanerNow Patch Management is a cloud-based endpoint protection system for cyber hygiene that provides the most recent automated security updates for Windows, macOS, and Linux-based devices. The vulnerability scanner is the critical component of this security services bundle. This system finds configuration flaws and passes the information to an automatic patch manager. SecPod SanerNow’s SaaS console, accessible from anywhere using any standard Web browser, is where the patch management is controlled.
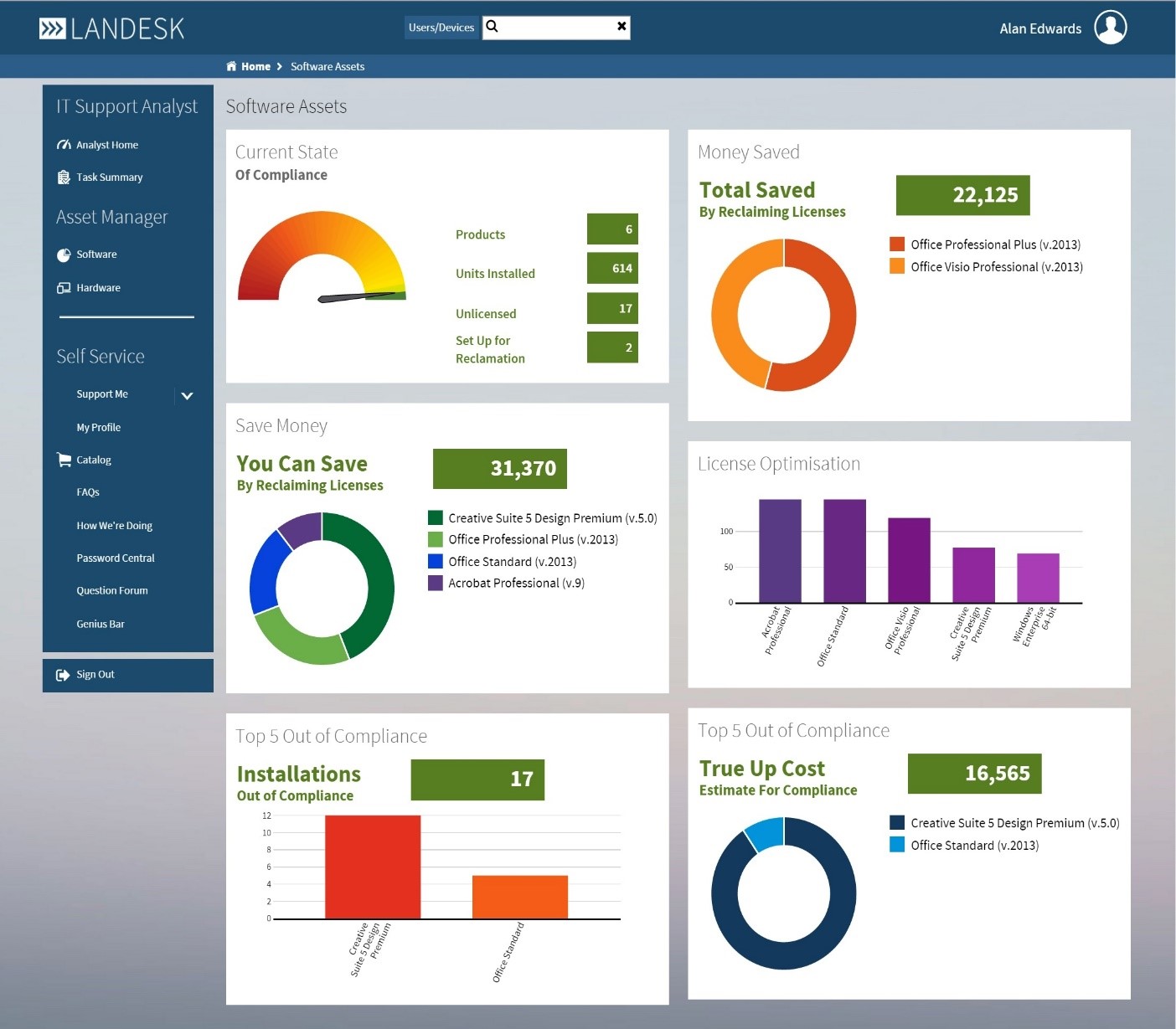
10. LANDesk Patch Manager
LANDesk is highly known among providers of systems and asset management software. One part of the company’s assortment of products is LANDesk Patch Manager. The best way to use Patch Manager is as an agent-based installation, giving you extensive network visibility. On computers running Windows, Red Hat, SUSE, and Mac OS X, find and fix vulnerabilities in the operating system and third-party apps. By integrating intelligence into an agent, the Wake-on-WAN feature of the solution eliminates the need for network configuration, improving patch success rates and speeding up automatic installation.