Information technology plays a role in bolstering national security against future threats and cyber-attacks. Information technology, in particular, may assist governments in identifying possible dangers. These are the top ten technologies used for information security.
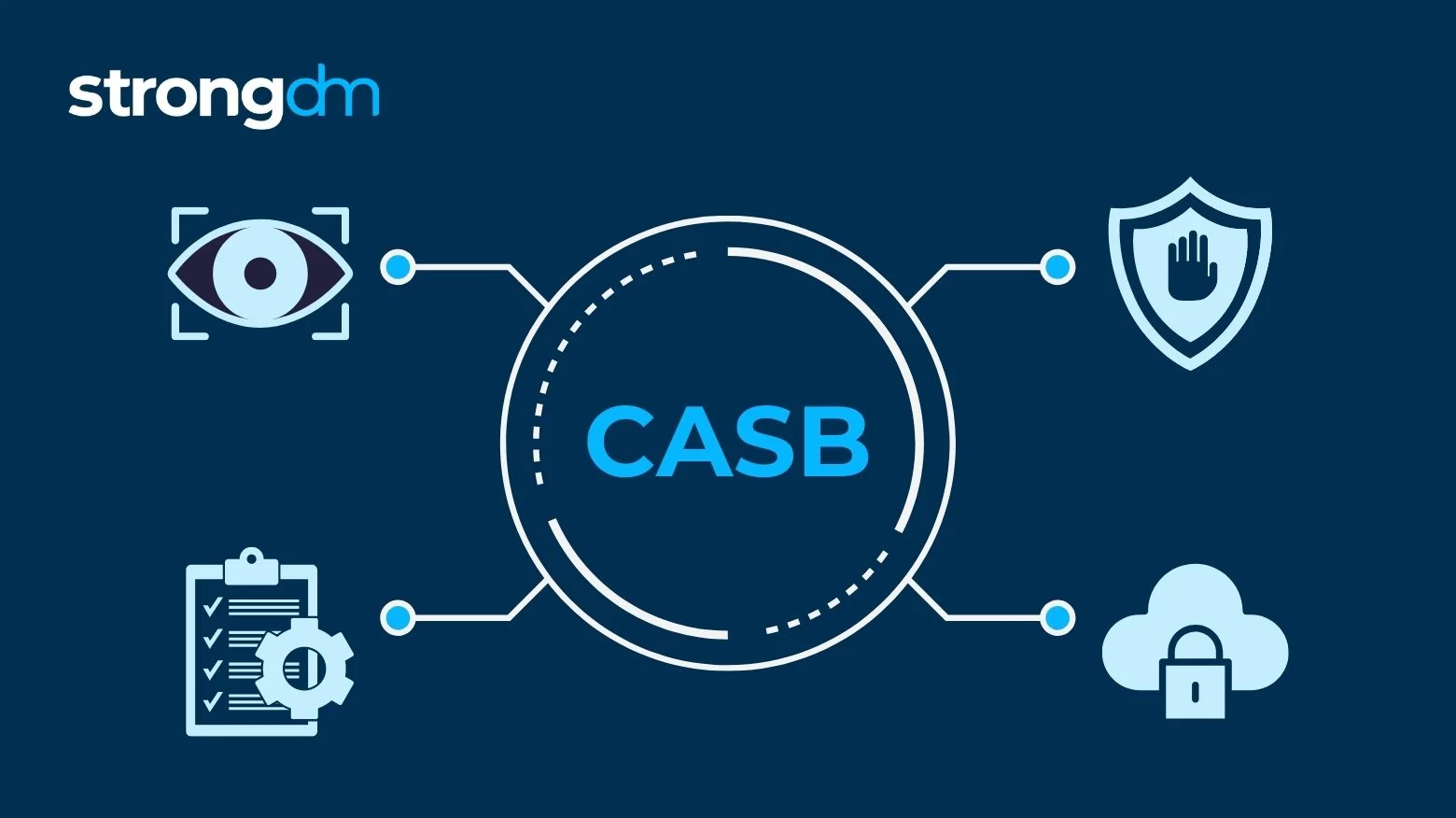
1. Cloud Access Security Brokers
Cloud access security brokers (CASBs) provide a control point for information security experts to use cloud services from various cloud providers securely and legally. Many “software as a service” (SaaS) products offer limited visibility and control choices, yet SaaS use is growing widespread in companies, exacerbating security teams’ displeasure with visibility and control. Many holes in individual cloud services are filled by CASB solutions, allowing chief information security officers to do so simultaneously across an expanding collection of cloud services, including infrastructure.
2. End Point Detection And Response
Endpoint and network events are recorded by EDR technologies and stored locally on the endpoint or in a centralized database. Databases with known indicators of compromise, behavior analytics, and machine-learning algorithms continuously mine the data for early identification of the threats and to respond to those attacks as swiftly as feasible.
3. Non-Signature Approaches For End Point Prevention
Purely signature-based malware protection systems are useless against sophisticated and tailored assaults. Memory protection and exploit prevention prevent the most common ways malware enters systems. Machine learning-based malware prevention, which uses mathematical models instead of signatures for malware identification and blocking, is among the techniques emerging to supplement traditional signature-based approaches.

4. User And Entity Behavioral Analytics
The use of user and entity behavioral analytics (UEBA) provides full security analytics, much as security information and event management (SIEM) enables broad-scope security monitoring. UEBA delivers user-centric analytics not just for user activity but also for endpoints, networks, and applications. The correlation of analyses across different entities improves the accuracy of the analytics and the effectiveness of threat identification.

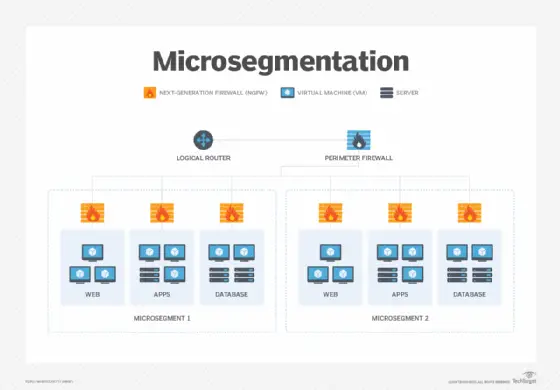
5. Microsegmentation
Micro-segmentation is a means of controlling network access amongst workloads that is secure. Administrators can use micro-segmentation to administer security policies that constrain traffic based on the principles of least privilege and No Trust. Businesses employ micro-segmentation to reduce the attack surface, improve breach control, and raise regulatory compliance.
6. Security Testing For Devops (Devsecops)
DevSecOps is a popular application security technique that includes adding security early in the software development life cycle. It also improves communication between development and operational teams, including security teams in the software delivery cycle. DevSecOps operating models are gaining traction, with scripts, “recipes,” blueprints, and templates driving the underlying setup of security infrastructure — including security rules such as application testing during development or network connection during runtime.
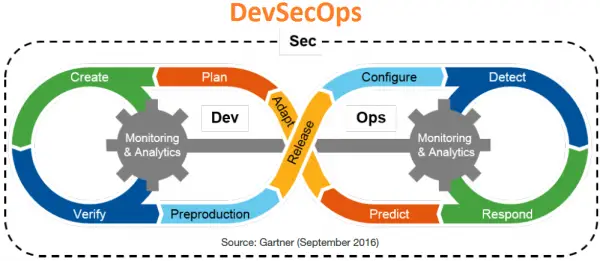
7. Intelligence-Driven Security Operations Center Orchestration Solutions
An intelligence-driven SOC must be designed with intelligence in mind and utilized to inform all aspects of security operations. To face the difficulties of the new “detection and response” paradigm, an intelligence-driven SOC must go beyond traditional defenses, incorporating adaptive architecture and context-aware components. To support these developments in information security programs, the SOC must evolve into an intelligence-driven SOC (ISOC), with automation and orchestration of SOC procedures playing a vital role.

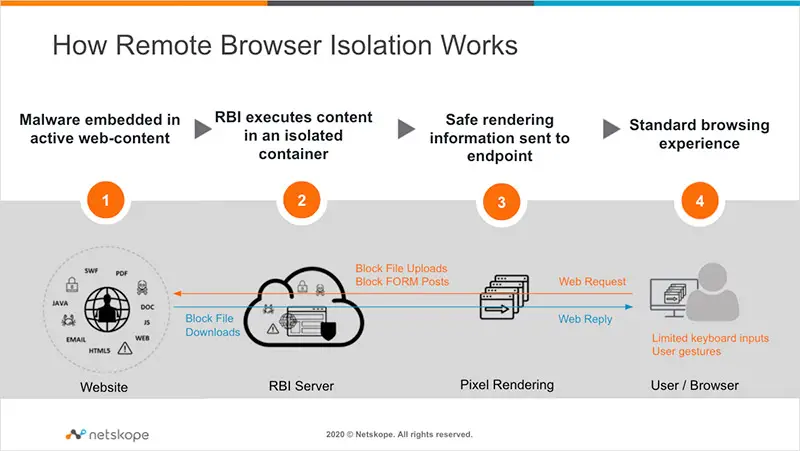
8. Remote Browser
A cloud-hosted browser is known as a “remote browser.” It allows users to access that particular browser on their computer systems from anywhere. The assaults begin by delivering malware to end users via email, URLs, or rogue websites.
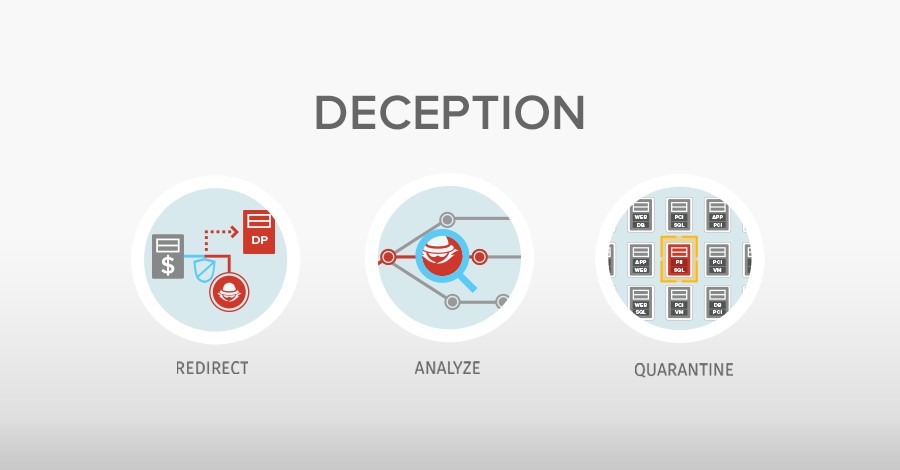
9. Deception
Deception technology is a cybersecurity defensive tactic that seeks to confuse attackers by disseminating a series of traps and decoys throughout a system’s architecture to simulate assets. The employment of deceptions aimed to throw off an attacker’s cognitive processes, disrupt an attacker’s automated tools, delay an attacker’s actions, or impede breach progression defines deception technologies.
10. Pervasive Trust Services
Trust services are carried out to scale and meet the demands of billions of devices, many of which have low computing power. Enterprises seeking large-scale, distributed trust or consensus-based services should prioritize trust services such as secure provisioning, data integrity, confidentiality, device identification, and authentication.

Conclusion
Information security, or InfoSec, refers to the methods and techniques devised and deployed to secure critical company information against alteration, disruption, destruction, and examination.