Drug development is a time-consuming, complicated, and expensive process with a high degree of clinical approval success uncertainty. Unidentified pathologies, a lack of patient stratification, and inaccurate models bring additional difficulties in this process. The pharmaceutical industry is implementing the newest technologies to get around them while maintaining efficiency and regulatory requirements.
1. Mrna Technology
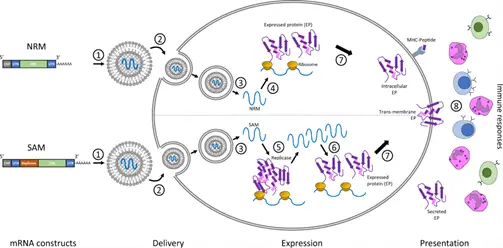
Because the new Covid-19 vaccines use this science, mRNA technology has recently received attention. MRNA vaccines give an alternative to the conventional vaccine approach due to their high efficacy, capacity for fast development, and potential for low production costs. Messenger ribonucleic acid, also known as mRNA, is a single-stranded RNA molecule that transports genetic information derived from DNA.
2. Virtual Reality
There has been the virtual reality for a while. But it is now used frequently to manage and treat various psychological disorders and ailments, from tension and anxiety to dementia and autism. By altering the way that patients think about and perceive pain, it is also used to manage pain effectively.
3. Neurotechnology
Numerous phases of life could be made better by Neurotechnology. It has many powerful future applications in various contexts, for example, education, workstation management, country security, and even in games and sports, additionally, the drug and medical fields, where it is already being employed in practice. Neurotechnology includes all components created to tackle the brain, visualize its functions, and even govern, fix, or enhance it.

4. Precision Medicine
Medical technology is evolving more and more individualized to particular patients as it develops. Precision medicine considers each patient’s unique genetic making, environmental factors, and lifestyle. For instance, a cancer patient may receive treatment specifically formulated for them based on their amazing genetic makeup, thanks to precision medicine.
5. CRISPR
The most sophisticated gene-editing method is Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats (CRISPR). It operates by utilizing the built-in defense system of bacterial cells’ immune systems, which can ” cut out” infected DNA strands. This DNA slicing can change how we approach disease treatment.
6. Telemedicine
Since the Covid-19 pandemic began in 2020, demand for telehealth and telemedicine has risen. While telehealth covers remote non-clinical services, telemedicine focuses on remote clinical services. Since the pandemic, more people have embraced new working and living practices, and by 2026, it is believed that the global telemedicine market will have increased from $68.36 billion to $218.49 billion.

7. Health Wearables
Since wearable technology first became known in recent years—specifically, since the launch of Bluetooth in 2000—demand for them has risen. Nowadays, people use wearables synced with their phones to track various things, including their sleep schedule, heart rate, and physical activity.

8. Technology In Mental Health
According to estimates, depression will account for most of the disease burden in the world by 2030, necessitating the development of new treatments more than ever. Many new technological developments that can assist in addressing patients’ ongoing mental health needs have evolved over the past year.

9. 3D Printing
One of the most known technologies on the market is 3D printing. These revolutionary printers in healthcare industries can make implants and even joints that can be used during operation. Additionally, the use of 3D printing is gaining popularity for preoperative planning. Surgeons can now attempt procedures they previously wouldn’t have been able to do, thanks to a realistic model of an actual patient’s anatomy.
10. Synthetic Biology
The area of drug development is being fundamentally reoriented thanks to developments in synthetic biology. Before beginning clinical trials, drug targets can be accurately screened using models created through genetic manipulation. Researchers can better comprehend the intricate interactions between genes and proteins thanks to gene editing and molecular biology.