During earlier times, there were no technologies for the agriculture sector that used to result in crop losses, consumption of more time for yielding, and many more disadvantages. Nowadays, we can observe technological advancements in the agricultural sector too. These advancements in the agriculture sector are meeting the growing demands of farm automation, digitization, efficiency for yielding, and reducing crop losses. Robots and drones are advancing agricultural automation by taking over manual farm tasks like harvesting fruit, pulling weeds, and watering plants. The top 10 technologies emerging for the advancement of the agriculture sector are penned in the article below.
1. Bee Vectoring Technologies
As the earth’s population is growing rapidly, Farmers need to produce 70% more food to feed us. Bee Vectoring Technology is an advanced technology for improved sustainable farming, better; crop yield, and improvement in soil quality. BVT technology uses fewer chemicals, less machinery, and no water. This process is carried out using a scientifically designed BVT tray. This technologically created bumblebee hive enables bees to pick up a tiny amount of pest control powders on their legs to disseminate as they move over the farm. A single bumble beehive contains up to 280 bees; these bees can touch approximately 9 million flowers over the bloom period. This method significantly reduces the number of control agents used in crop spraying, which makes it superior to crop spraying. BVT is a sophisticated solution to a challenging issue.

2. Internet Of Things
Internet Of Things technology has brought a revolutionary change in the agriculture sector. The term Internet of things describes objects or gadgets that have integrated sensors into them so that they can transfer data across a network. IoT devices assist farmers in monitoring farm performance and operations and helping them make better decisions to boost farm productivity and production. Additionally, IoT devices assist in automating agriculture irrigation. IoT devices can gather information like chemical application, weather, cattle’s health, and how much fertilizer to apply to crop and dam levels, thus resulting in less cost and saving time.

3. Agricultural Robotics
As the world is developing, the; lack of farm laborers has been a crucial problem today faced by the farmers. Thus automation comes into existence to make farming easier. Start-ups; are developing agricultural robots that reduce manually carried-out tasks such as harvesting, yielding crops, weeding, checking weather conditions, humidity, soil fertility, crop quality, spraying, planting, and transplanting. Farmers rely on agricultural robots these days as these robots thus result in the reduction of human error and no inconvenience caused. In addition, they produce autonomous tractors and hybrid electric drive systems that help farmers automate massive tasks with little effort and time.

4. Real-Time Kinematic Technology
Real-Time Kinematic Technology is a technology used for measuring accuracy. While the GPS can pinpoint your location with an accuracy of two to four meters, this technology can do it with centimeter-level precision. Real-Time Kinematic Technology utilizes two receivers, one of which is a base station, and the other one is a rover. The base station is a receiver installed at a location whose precise position is computed; by other independent precision methods. RTK is, used for applications that require higher accuracy as conducting surveys, construction activities, and drones.

5. Drones
The world’s most arable land is in India. Consequently, there is a higher amount of farming. Drones have brought a revolutionary change in the agriculture industry. Drones make it possible to acquire data on things; like which crop is ready for harvest, how much fertilizer has to be; given to the crops, and the degree of production. Both efficiency and farmer safety is increased by double. Drones reduce overall costs. Drones that can monitor soil, field planning, weed pressure, chlorophyll levels, and the mineral and chemical balance of the ground are also being; developed by start-ups.

6. Precision Agriculture
Precision farming is a technique that uses a precise amount of water, and maximizes the efficiency of water, fertilizer, and pesticides to improve overall productivity, quality, and yield. Israel is the biggest; example of Precision agriculture. Due to this development in agricultural technology, farmers can modify crop production factors, such as moisture content, soil quality, and microclimates to maximize output, which uses big data to support management choices. To increase crop output and maximize agricultural resources, it uses robots, automation, drones, and remote sensing devices.

7. Indoor Vertical Farming
Farmers used to perform traditional farming manually, but as the human population has grown over the past few centuries and the need for food has increased, pressure has been placed on Traditional Farming to enhance food production. The traditional farming method requires acres of space for crop production. However, in Vertical Farming, acres of land get condensed into the size of a big box retail store. Water is recycled and used again for other crop production. Thus a lot of amount of water is saved as compared to traditional farming.
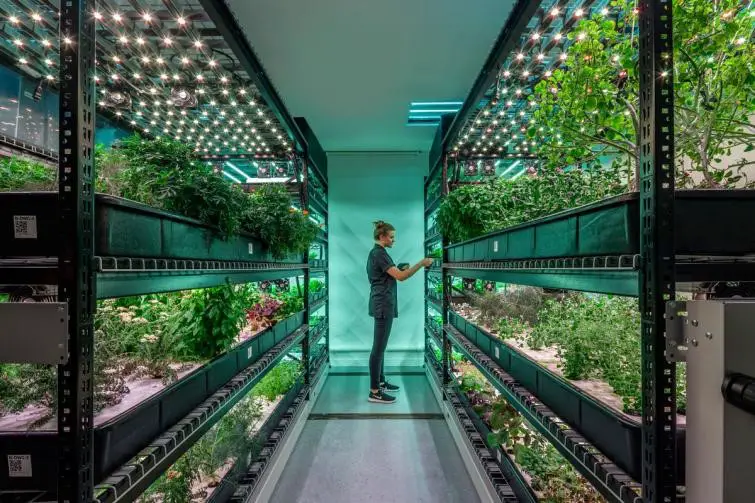

8. Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence plays an important; role in the agriculture sector too. Artificial intelligence is used to monitor crop health and crop productivity. Insects transfer bacterial, viral, or fungal infections to the crop, resulting in crop damage. Drones monitor hazardous pests on crops and spray pesticides as soon as they get detected by drone technology, which uses artificial intelligence. Artificial Intelligence includes applications like monitoring livestock health, soil diagnosis, monitoring crop readiness, etc.
9. Regenerative Agriculture
Traditional farming methods cause soil to crust over and erode over time; Soil doesn’t get time to recover before the subsequent growing season because of overgrazing, Tilling, and Plough. On the other side, regenerative agriculture prioritizes boosting soil biodiversity and causing little to no soil disturbance. It includes a variety of techniques, including crop rotation, no-till farming, and reduced tillage. For instance, to reestablish soil fertility, cover crops are sown to cover the land in-between cropping seasons.

10. Big Data & Analytics
The current state of agriculture involves a lot of guesswork or predictions for crop production. Analytical tools utilize data on weather events, agricultural machinery, water cycles, crop quality, and crop amount to derive information pertinent to farming operations. Several firms are providing agricultural analytics tools that help farmers make the most of their field data. Data analytics help to reduce crop losses, increase efficiency in crop production, soil fertility, etc.



















