In the present digital era, the User Experience (UX) and User Interface (UI) design are behind any product or website’s success in the market. Developing an interactive and seamless user experience helps in retaining maximum users while attracting new customers. It also provides a sense of security and loyalty to the customers and other partner brands to increase the business. An ideal user experience is achieved by sticking to already-established principles that help in the design process. In this article we will learn about the Top 10 UX/UI Principles that can help boost the user experience efficiently:
1. User-Centered Design
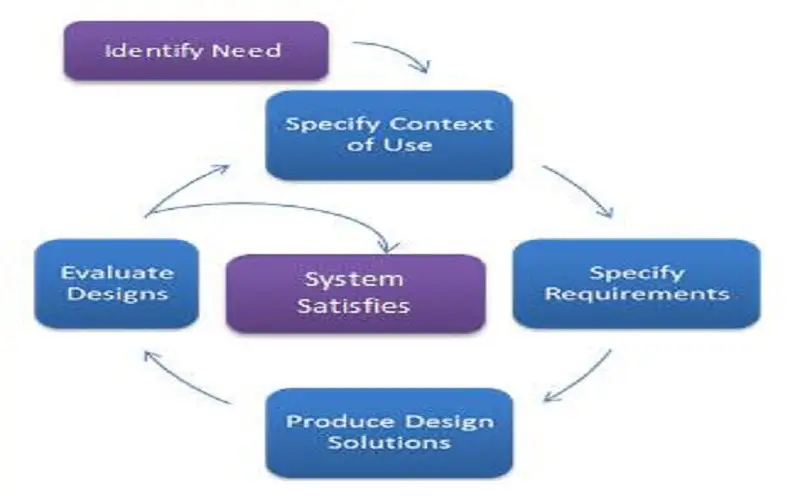
The base of the UX/UI design process revolves around the center of the users that will access the product or service. To understand the needs and mindset of your users thorough research is needed by gathering feedback from them. This approach allows the design to be appealing to the users in a way that fosters their preferences. This makes it an essential prerequisite to align your design choices with the behavior and needs of the target audience so that the product can be sustained for the long term.
2. Clarity And Simplicity
Unnecessary complex designs that make things cluttered should be avoided since they degrade the user experience. The fundamental principle in UI/UX designs is to keep things as simple as possible since a clean and straightforward approach enhances the usability and aesthetics of the finished product. Some of the key points to remember are to utilize white space effectively, deploy a consistent layout, and keep navigation simple. This provides users with a clear and intuitive pathway through the product or website.

3. Consistency
Consistency plays a vital role in creating an ordered and smooth user experience. This includes maintaining color themes, typography, and design elements throughout your product or website to give users an impression of professionalism. It can drastically generate a new customer base and help them feel more comfortable when they use the interface. The learning curve of the final product and the cognitive load that it imparts gets eliminated by a huge fraction if the design is consistent and simple.

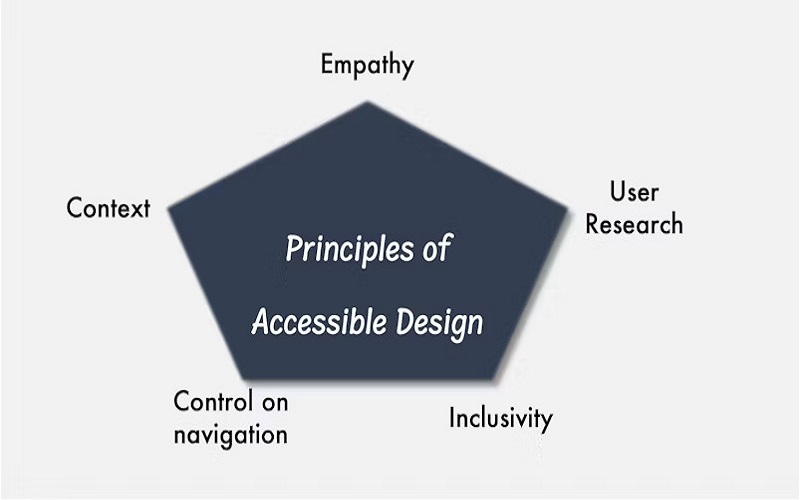
4. Accessibility
Designs should be made while keeping the inclusivity of all sorts of target audiences in mind. This involves making sure that your product or website is accessible to all users running different platforms including people having disabilities. This is achieved by deploying features like alt text for images, structural headings, and keyboard navigation. Not only does it widen your customer base but it also represents a dedication to make ethical designs.
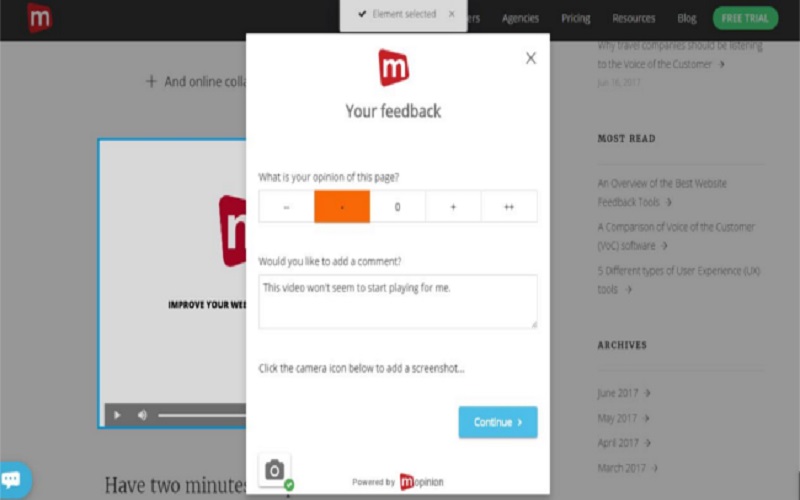
5. Feedback And Affordance
It becomes important to incorporate a feedback system for users to understand the result of their actions. This is done by informing users by implementing visual and auditory gestures or representations upon their interactions. Moreover, it is accompanied by affordances that are elements specially designed to guide users to surf the site. For example, a clickable button that should appear visually different from the non-dynamic text.
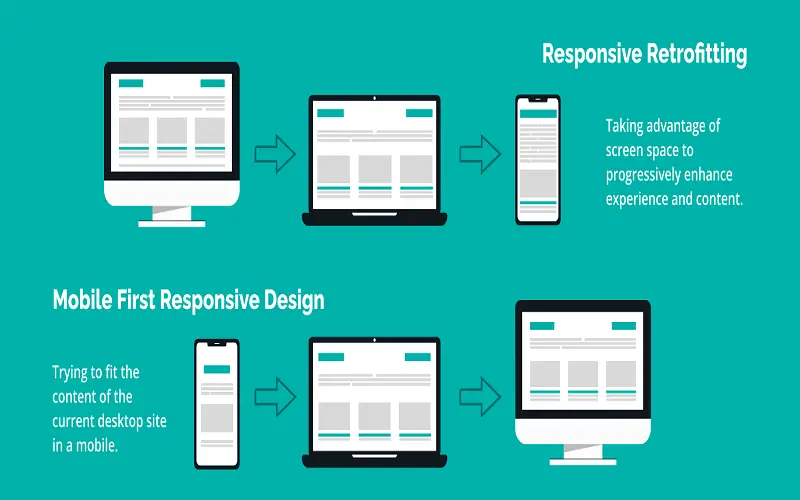
6. Mobile-First Design
With the availability of personal mobile devices in every part of the world, it becomes natural to adopt a mobile-first approach. The best practice is to start designing for mobile screens and then focus on scaling up for larger devices. A working website should have a responsive design that is compatible with all devices to ensure your product and its functions reach the audiences on their respective devices smoothly. This needs to be done by still maintaining the consistency and uniformity of the website so that it does not appear distinct regardless of the device used.
7. Load Time Optimization
With the development of quick technologies in recent times, users expect the loading times to be low for their convenience. So a high-performance design that prevents users from getting annoyed due to slow loading times plays a crucial role in achieving user satisfaction. Some of the ways by which this can be solved are to compress images, less HTTP requests, and improve caching in the browser. This ensures optimized loading times and also keep the users engaged without any issue.

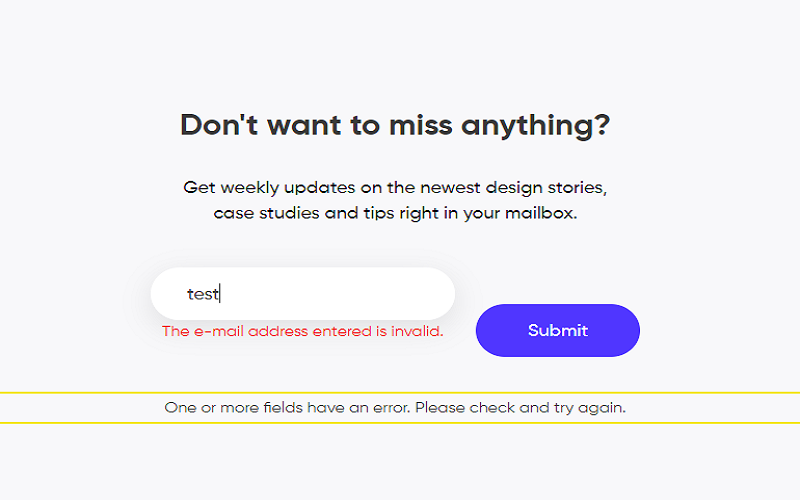
8. Error Prevention And Recovery
While designing a project and maintaining an industrial standard some errors are bound to appear for the designer. Easy-to-read error messages that help users mitigate these errors should be used to uplift the user experience as a whole.The design should be made in a way that anticipates these errors and provides an option to undo actions and fix these errors if any occur. If a design is developed in such a way that manages error handling efficiently it can transform a frustrating user experience into an enjoyable one.
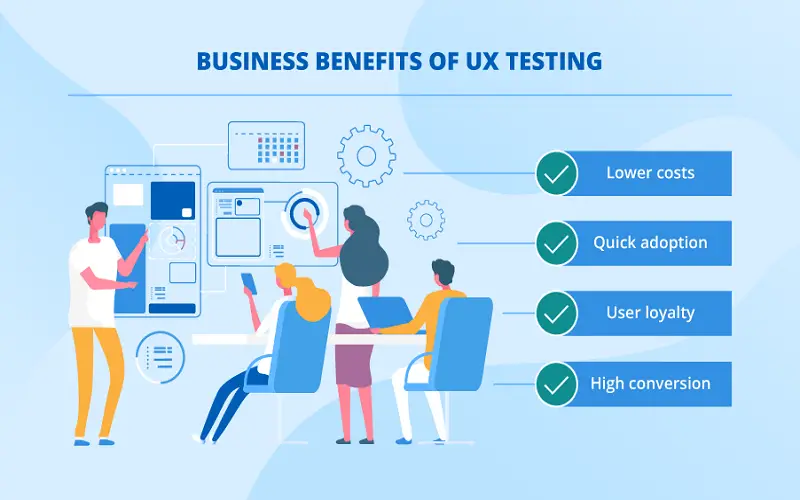
9. User Testing And Iteration
A design is never a complete finished product since there is always room for improvement here and there upon receiving user feedback. This process is instead an iterative one that requires regular testing of the product or website with real users to recognize the key points and such areas of improvement. These feedbacks and results are stored in a database which is analyzed to enhance the design in further elevating the business opportunities and the user experience together. This makes user feedback an invaluable asset to refine your design and make sure it lives up to the expectations of the users.
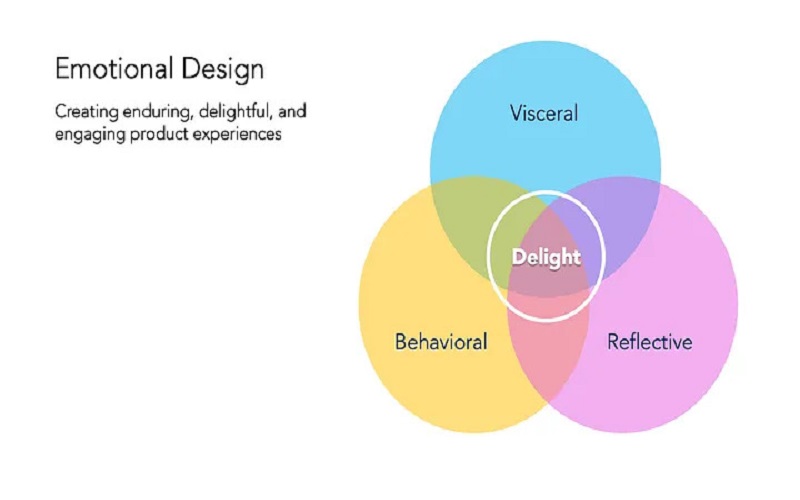
10. Emotional Design
Last on the list is to grab the potential emotional influence of the design on the users. Emotions strongly influence user behavior and their preferences when choosing a product or a service, especially in India. This aspect should be utilized in design elements that send positive emotions, such as delightful animations, customized experiences, and visually appealing structures. In this way, the product marks a lasting impression on the users making them feel connected with it. Also, the retention frequency of the users can be increased dramatically if this is carried out effectively with all the other principles together. The key to successful design is continuous improvement and meeting user expectations by making the service relatable or appealing to the target users.