Biometric confirmation alludes to the security strategy that includes interesting natural characteristics of people such as retinas, irises, voices, facial characters, and fingerprints to confirm individuals are who they claim to be. It handles control access to physical and advanced assets, such as buildings, rooms, and gadgets. Biometric verification works by comparing two sets of information.
1. Fingerprint Scanning
Fingerprinting is distinguishing a person’s personality by comparing two fingerprints. Unique mark acknowledgment is one of the foremost well-known biometric innovations and is the foremost utilized arrangement for character confirmation in computer frameworks. Fingerprints are used since they are simpler to obtain compared to others.

2. Voice Recognition
It is checking of innovations centers on vocal characteristics to recognize one individual from another. Voice are captured in a database, and a few information points recorded as parameters for a voiceprint. Advances in speech recognition focus on mouth and throat shape placement and sound quality rather than just tuning to the voice. It makes a difference and reduces the chance of voice mimicry attempts being misunderstood.

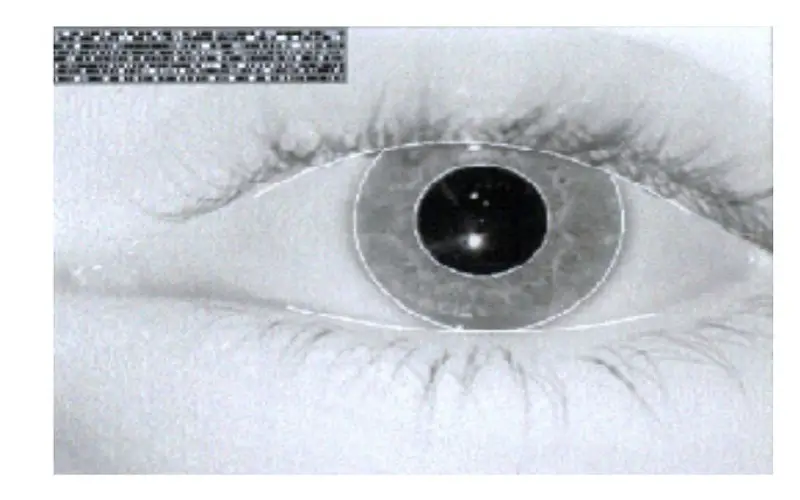
3. IRIS/ Retinal Scanners
Iris acknowledgment checks work by using a special light that illuminates the eye. This process stores information about a unique look in a database that verifies their identity later. Retina acknowledgment uses specific light on blood vessels at the back of the eyeball. It helps in visualizing the shape of the blood vessels. Iris and retina acknowledge checks use the wrong coordinates because they are hard to replicate visually. As a result, they are critical to ensure the safety of high-security facilities such as government and military buildings.

4. Facial Recognition
Facial recognition works better with costly technology but not in unconventional situations. Besides this plan, it seemed inefficient because it permitted confirmation that was easy to get.

5. Handwriting Recognition
It is brought into use where tasks are performed sequentially, such as in banks and courts. With signature recognition, a computer uses special tools to check a person’s signature. The computer looks for patterns to create the signature and uses numbers to understand them. It confirms the signature by looking at the shapes and lines. These methods help simplify time series by breaking them down or using curved lines.

6. Hand And Finger Geometry
Our hands are distinctive to us and different from other people’s if we do not have fingerprints or eye scanners. The deployed hand scanner works by measuring important hand characteristics, such as the size of the palm, the length of the fingers, and the space between the knuckles. The system’s advantages include its affordability, simplicity of construction, and lack of side effects. Because hands are not distinctive, the system isn’t accurate.

7. DNA Based
Using genetic analysis to identify individuals makes DNA a viable method of identification. No two humans are genetically identical, as DNA is the blueprint for our physical and cognitive traits. Despite the widespread DNA identification techniques, they aren’t entirely accurate. The individual’s identification code is altered due to the lack of DNA researcher’s care.
8. Vein Geometry
The configuration of the blood vessels in our anatomy is unique, and characteristic identical siblings do not have arrangements. Veins have been considered beneficial due to their inherent difficulty mimicking them, primarily due to their visibility in regulated environments. The machine suited to this task is a vein scanner that uses different light modalities to visualize images of individual veins.
9. Behavioral Identifiers (Typing Recognition And Gait Biometrics)
Typing recognition analyzes a person’s typing style, including typing speed and keyboard pressure, to identify them. Gait recognition is the technique of recognizing people based on their gait patterns. Clever paraphrase: The analysis focuses on factors such as movement speed and the use of their bodies. Gait can identify people without physical contact and differs from fingerprint and iris recognition methods.

10. Eye Recognition
Eye recognition involves visual analysis to identify the individual examining their eye characteristics. This method includes utilizing the different patterns in an individual iris or retina. Identity authentication features are comparatively less common, likely due to the greater complexity of setup procedures. Achieving high precision in iris recognition requires a lighting system, a camera with enhanced vision capabilities, and minimal interference from ambient light.