Air pollution control devices (APCD) are not just a few pollutants, but some devices are used to prevent gases and solids, especially outside of industrial cells. These control devices can be divided into two main categories: (a) devices that control the amount of part of the environment that escapes the environment, and (b) devices with controls that emit acid gas into the atmosphere.
In general, atmospheric pollutants are generated in the fuels of fuel fuels. Following are the air pollution control devices:
1. Dust Catcher
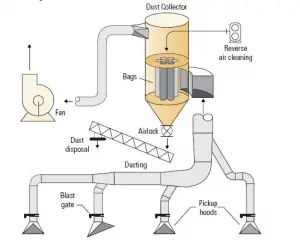
The inner construction of the shafts changes the direction of the exhaust gas flow. This causes the dust particles to be distinguished by their greater momentum. Separate particles compete with gravitational force.
The solar collector collects particles in liquid liquids up into the air. They are often used in the collection of metal fluids and sodium or oil pastes. Solar collectors are usually used to improve the quality of the air or the work environment.
Smoke and smoke collectors use micrometers to remove air particles. Efficiently reduce or reduce particulate matter and gas flows in many industrial processes.
2. Cyclones
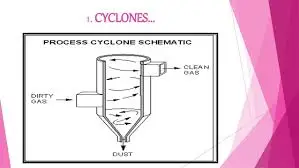
It uses the method of separating cycles to eliminate the gas particles. The particles that generate gas emission flow are emitted in a spiral wagon in a cylindrical load. Dirty gas leaks into the chamber on the outer wall of the tangential outer device, the whirlpool goes into a room. The centrifugal force generated by the circulation circulates with the particles of the cyclic wall powder. After hitting the wall, the particles fall on a low tile.
Large particles move beyond their inertia and force them toward the wall of the chamber. When the friction is reduced to the surface of the wall, the dust at the foot of the cycle slides down to a conical plate. Leaking clean gas flows up through an inner cylinder through a deeper spiral and greater outlet and the periodic isotope of particulate particles are eliminated from the folds at the bottom.
There is approximately 90% efficiency with more than 20 micrometers of particles. However, the cycles are not enough to meet the air quality standards.
3. Fabric Filters
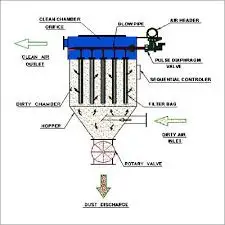
The fabric filter is also called baghouses. They use leakage filtration to separate dust particles from gas pumps. Dust collectors are the most efficient and most profitable. Dust-filled gas filters incorporate a cloth filter and filter through cloth bags that work as a filter. Woven or lined cotton bags may be made of synthetic or fiberglass materials in the form of a tube or wallet. These filters are highly effective due to the cake powder made on the surface of the bag.
The combination of these mechanisms creates a powder cake in the filter, which finally increases the flow of gas through the resistance. The filter should be cleaned regularly.
Hundreds of dust filter collectors can have as little as 0.5 micrometers of small micrometers and a large number of particles. However, the cloth filter offers some gas resistance and is expensive to operate and maintain. Also, to maintain the filter cloth, cooling is required for exhaust gas (generally less than 300C) before passing through the refrigerator. The necessary cooling coil increases the cost of capital. Also, some filter fabrics (for example, ceramic or mineral materials) can work at higher temperatures.
4. Electrostatic precipitators

The electrostatic blower is a particulate collection device, which removes particles from the gas emissions (such as exhaust gases) through the induced electrostatic charge. ESPs are high-efficiency filtration devices that prevent the flow of gas through the device and easily eliminate fine particles from the gas network. It only applies energy to collect ESP particles and therefore is very energy efficient (in the mode of electricity.)
They comprise ESPs (i) deserters to break the gas flow, (ii) collecting and collecting electrodes, (iii) dust cleaning system and (iv) collection funnels. The high voltage of the DC is applied to the charge of the electrode to charge particles because they are attracted by the opposing combustion electrodes.
In a typical ESP, the electrode of the collection is composed of a large rectangular metal, in a structure of a suspended box vertically and vertically in parallel. Normally, in hundreds of strips, there is a combined surface of about 10,000 m². The lines of electric charge lines must be between the collecting plates. The cables obtain a negative electrical charge; the plates become a base, so they are charged positively.
The particles that are attached to the plate in the collection will be removed regularly by shaking or “touching” the plates. Friction is a mechanical technique for the separation of captured particles, which usually cover 6 mm poles.
5. Scrubbers

The exhaust gas may contain substances harmful to the environment, and the purifier may eliminate or neutralize these substances. Waste systems are a distinct APCD. Traditionally, the term “washing machine” is being channeled into liquid pollution control devices, which use liquids to clean unwanted liquid gas pollutants. Garbage is one of the main devices that control gas emissions, especially acid gas. Washing machines can be washing machines or washing machines.
The humidifier purifier describes the exhaust gas that describes different devices that eliminate the contaminant gas flows. In a wet residue, the gas stream is usually infused (i) in contact with the spray of fluid, which is poured into the liquid, (ii) forcing the liquid group, or (iii) a contacting method for removing pollutants. The growth design of treatment depends on the nature of the process conditions and the pollutants. The characteristics of the inlet gas and the properties of the powder (when the particles are present) are important.
Wet scrubbers remove dust particles by capturing droplets of liquid. Wet cleaners are eliminated by the dissolution or absorption of liquid pollutants. All drops in water gas treatment plants must be separated from the outlet gas network or drawn by a separate device called a separator (these terms are interchangeable). Also, the netsplit must be treated before discharge or final reuse.
6. Incinerations
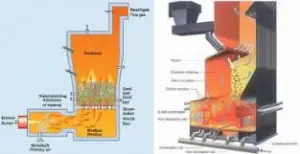
Waste treatment is incineration related to the combustion of organic substances contained in the material waste. Higher temperatures and other temperature treatment systems are described as “heat treatment.” The incineration of waste becomes waste in ashes, combustion, and heat. Ashes from a predominantly inorganic component of the residue and can take the form of lumps or solid particles collected by combustion gas. The combustion gases must be cleaned with gases and particles before dispersing into the atmosphere. In some cases, the heat created by incineration can be used to generate electricity.
The incineration of energy recovery is one of the main technological disadvantages of energy, gasification, pyrolysis and anaerobic digestion. The fuel gas is the main energy product of gasification. Training and gasification can also be implemented to recover energy and materials.
In several countries, there are still concerns about the environmental effects of smoking and local communities (see arguments against incrimination).
In some countries, the fact that incinerators were separated less than a decade ago is not to eliminate reactive, bulky or recyclable materials. These facilities compromised the health of the factory workers and the local environment due to the low level of combustion gas combustion.
7. Carbon Capture

Carbon capture and storage (CCS) (or capture carbon or carbon capture and capture) carbon dioxide (CO2) waste out of the process, for example, energy from the storage site fossil plants with transport and the atmosphere does not fit it in place, usually underground geological formation While CO2 is included in several geological formalizations, for decades, including recovery from oil improvements, long-term CO2 storage is a relatively new concept. The first commercial In 2000, Weyburn-Middle was a carbon dioxide project. Dam You can also use ‘CCS’ to describe atmospheric air purification as a CO2 climate engineering technique.
The CCS integrated into the pilot center continued the German power plant Schwarze Pumpe, managed by utility Vattenfall, to test the technological viability and economic efficiency.


















