What is Microsoft Exchange Server?
Microsoft Exchange or Microsoft Exchange Server is a calendaring and mail server that exclusively runs on Windows Server (such as Windows Server 2003, Windows 2000 Server, etc.) Operating System. It was developed by Microsoft Corp. and was first released on April 11, 1993. Initially, it was an internet mail server from Microsoft. The Exchange Server 4.0 was the very first version of Exchange Server that was published outside Microsoft. It initially used the ITU-T Recommendations suite called X.400, but later shifted to Microsoft’s Active Directory (AD). Newer versions such as 4.0 and 5.0 were bundled with Microsoft Exchange Client; however, it was stopped in favor of MS Outlook.
Exchange Server uses Messaging Application Programming Interface (MAPI), an API-based Component Object Model, which allows the user to send an email inside a Windows application and attach the file to the e-mail note. Subsequently, it also supports POP3 (Post Office Protocol 3), IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol), SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol), and EAS (Exchange ActiveSync).
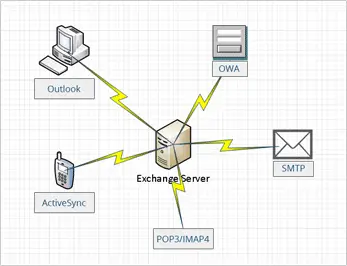
Exchange Server can be acquired through on-premises software or software as a service. The on-premises software means the customer bought a commercial software license called Client Access License (CAL). They can use the service by connecting to server software. Whilst the software as a service means the customer is required to pay a monthly service fee to use the service.
Before Exchange Server, Microsoft had already sold several email-based products, but Exchange Server is a contemporary client-server mail system, which is based on X.400 and also supports the X.500 directory services. Eventually, Exchange Server uses Active Directory (AD), a Microsoft directory service that is acquiescent to LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol). It is amalgamated into Windows 2000 as the infrastructure of Windows Server domains.
The following are Exchange Server’s released versions:
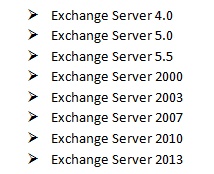
The Exchange Server 4.0 had released 5 Service Packs (SP1, SP2, SP3, SP4, and SP5) over the last two years. The Exchange Server 2007 was the first version to require Windows Server x64.
Uses of Microsoft Exchange:
Over the years, Exchange has now become Microsoft’s very popular messaging system that has a mail server, groupware applications, and email program. It is specifically designed for business use. The Exchange Server is generally utilized in conjunction with MS Outlook; to possibly use its collective features including its capability to share contact lists and calendars.
Exchange Server also provides an easy-to-use and a steadfast messaging platform. It helps the companies in minimizing help desk and fixed administrative costs using its administrative functions.
Microsoft Exchange Server also offers considerable security than the fax or mail communications. It enables businesses to secure their customer’s sensitive data and allows retention, archiving, and a leakage protection.
Exchange Server 2016:
Microsoft Exchange Server 2016 was released in October 2015. It is the current version, which introduces several helpful features and services including the following:

- Outlook on the web: it is Microsoft’s Personal Information Manager (PIM) web app. This is included in Exchange Online, Exchange Server, and Office 365. It is now optimized for Smartphones and tablets, in addition to laptop and desktop PCs.
- To communicate with Exchange, Outlook now uses the default protocol, MAPI over HTTP. This feature improves stability and reliability of Exchange and Outlook connections.
- Office 365 Hybrid: From the old Hybrid Configuration Wizard (HCW), which was included in the 2013 version, Exchange has now moved to a cloud-based application. When a user is selected to configure Exchange 2016’s hybrid deployment, he or she will be asked to install the wizard as a small app. It works just the same as the previous version but with added functionalities such as an improved diagnostics and troubleshooting for resolving issues when running the wizard, a quick process to update the wizard, etc.
- An updated and well-improved message policy and compliance features.
- The collaboration of Documents: the on-premises users can combine the files, the same way that it works in Office 365.
Click here for the complete list of What’s New in Exchange 2016.