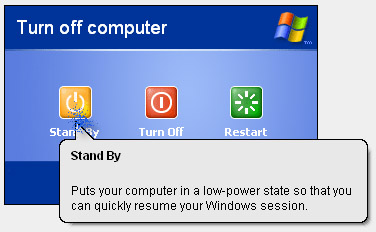
Functions of Stand By button in Windows XP

When we click Start menu then "Turn Off Computer. ” then “Turn off computer” window comes.
What is the function of the “Stand By” button in windows XP?