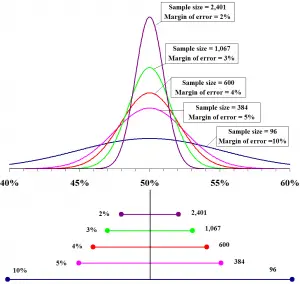
Process Required In Calculating Sampling Error In Linear Regression

For my computer science project I am studying linear regression. There is the concept of calculating sampling error in that topic. Please help me understand how to calculate the error.