
What is a stub network? What is the objective of configuring a stub network? How does a Stub Network link with the internet? How is it different from a LAN? With reference to a stub network explain what is an OSPF? How does an OSPF decide a network to be stub? What is a stub autonomous system?
A stub network uses a single entry exit point to communicate. Why?

Stub network is the term that describes the computer network or a part of a network without the knowledge of other networks. The stub network contain only one default path to non local hosts. A single logical path is used for the outward and inward traffic flow in a network of a non local stub. The stub networks functions similar to that of LANs. Examples of stub network are- individual group which uses only one router, organization level LANs etc. Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) is a routing protocol which is used in Internet Protocol(IP) networks. The implementation OPSF can be done by link state routing algorithm. OPSF sends protocol messages. The stub networks can be distinguished from other networks by the router address number. The stub autonomous system is one that is connected to other autonomous system to make access the internet.
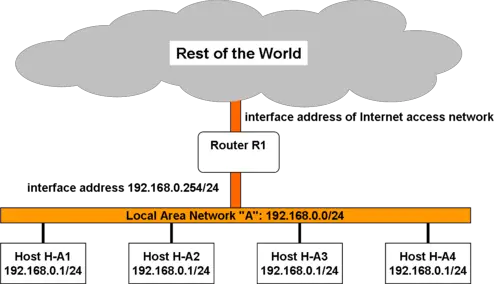
A stub network uses a single entry exit point to communicate. Why?

A stub network is an internal network, normally a local area network or LAN that transports data packets between local hosts only. It doesn’t transport traffic for other networks even if there are paths to more than one other networks. The data on a stub network is intended for an endpoint placed on that network.
The flow of network traffic in a stub network is local. The network traffic is local in the sense that it doesn’t travel outside the internal network. A single logical path is used for non-local network traffic when traveling in and out of the network. One example of a stub network is a local area network that never transports multiple router data packets.
The data traffic is forever to or from local hosts.














