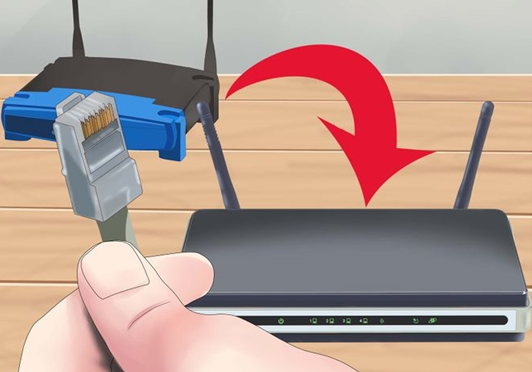
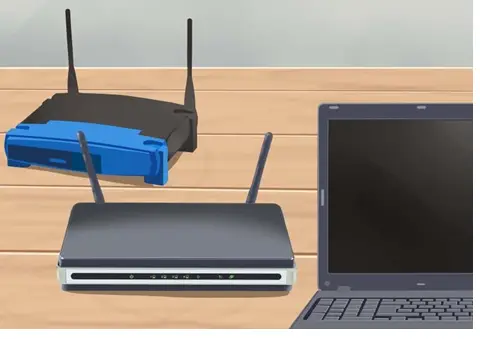
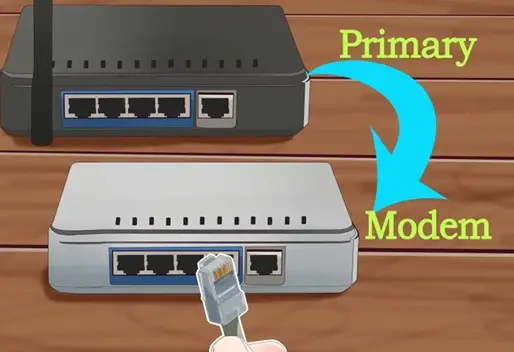
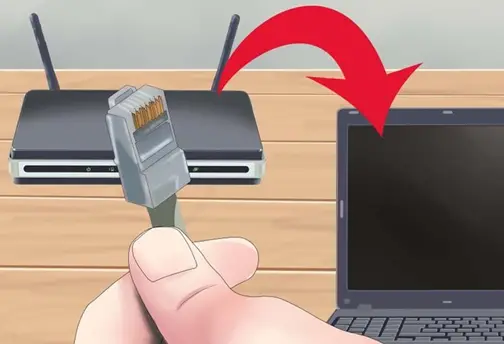
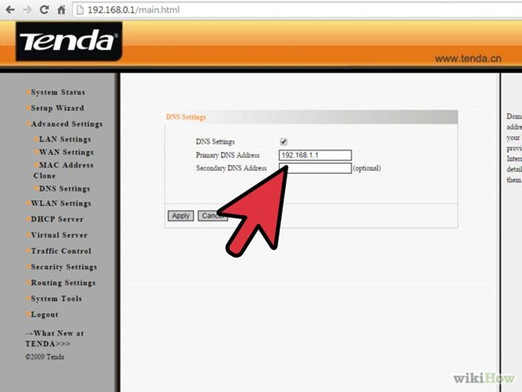
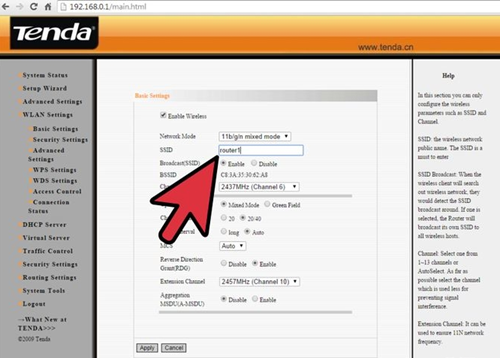
Is there any way to setup two routers in a house?

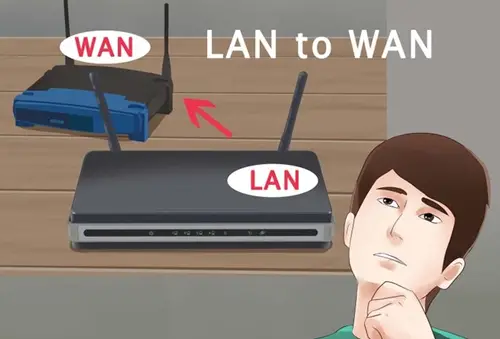
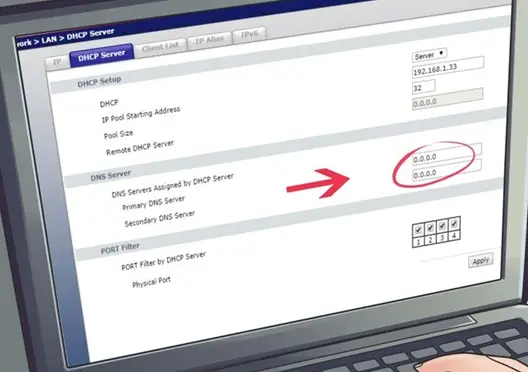
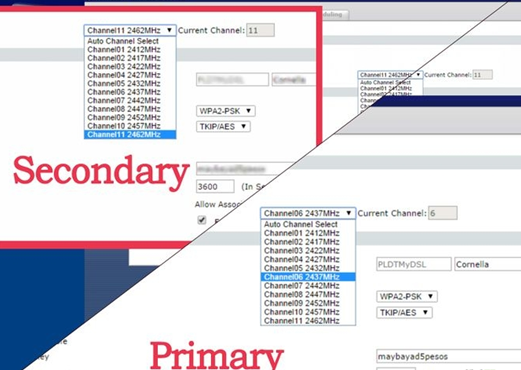
I have recently moved to a new house and setup a router to run WiFi. But due to some problem in the designing of house I am not able to use internet throughout the house. The signal only stretch through half of the house. Is there any way to setup two routers in different parts of the house with the same Internet?