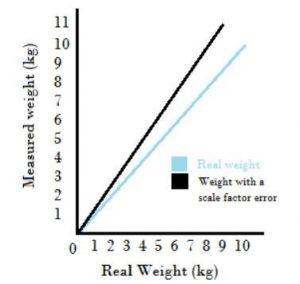
Understanding The Systematic Errors With Examples For Studies

I am not able to understand the difference between systematic error and the random error as I read both of them I and got confused. Would I like to know about examples of systematic error?